ANTITUSSIVE EFFECT OF
DEKOFCYN
ON CHRONIC COUGH
by
Dr. T. B. MASTER, M.D. (BOM.), T.D.D. (Wales), F.C.C.P. (U.S.A.)
Hon. Professor of Tuberculosis, Hon. Physician, Department of Tuberculosis, Group of T.B. Hospitals, Sewn, Bombay.
J. J. Group of Hospitals and Grant Medical College, Bombay.
Dr. K. C. MOHANTY, M.D. (Chest), T.D.D. (Born.)
Hon. Asst. Physician, Group of T.B. Hospitals, Sewn, Bombay.
Dr. J. M. SHRIMANKAR M.B.B.S.
With the increase in industrialization and road traffic, there is a corresponding increase in air pollution resulting in irritation of the respiratory tract, leading to chronic cough with or without expectoration. The cases of non-specific bronchitis are on the increase in clinical practice. Cough is also a problem in pulmonary tuberculosis, chronic bronchitis, etc. The medical remedies available either contain only expectorants, mixture of expectorants and sedatives, sedatives and bronchodilators. All these preparations give the patient temporary relief. Moreover, very often the clinicians have to use antibiotics along with it. Prolonged and frequent use of antibiotics, leads to toxic symptoms as loss of intestinal bacterial flora, blood dyscrasias and other toxic symptoms. It is also expensive to the patient.
Dekofcyn (Alarsin), an Ayurvedic preparation, is claimed to have good curing effect on chronic cough patients. It is also claimed that it does not hinder expec-toration, does not depress respiration, does not cause sedation, does not cause constipation or gastrointestinal upset and besides it acts as hemostatic. The individual drugs in Dekofcyn are used especially for chronic cough, chronic low-grade fever and general weakness, in Ayurvedic medicines.
This study is undertaken to assess the effect of Dekofcyn in patients having chronic cough for more than one month and not responding to usual routine treatment. The patients were taken in two groups, 20 patients having tubercular infection and another 20 patients having no tubercular infection. The patients were given Dekofcyn, 2 tablets t.d.s. for 21 days.
MATERIAL AND METHOD
The study was conducted at J. J. Group of Hospitals, T.B. Clinic, Bombay, at the domiciliary level.
Selection of the Patients:
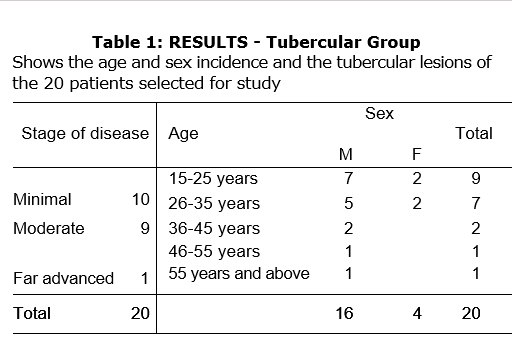
- 20 tubercular patients were selected for the study. The following criteria were observed for the selection of patients. a. Having pulm. T.B. lesion radiologically. b. Not less than 15 years of age. c. Weight not less than 30 kg. d. No other associated systemic disease. e. Not addicted to alcohol, cigarettes. f. Having cough for more than 1 month duration and not responding to usual routine treatment.
- 20 non-tubercular patients were selected accord-ing to same criteria. The following examinations were carried out at the time of admission and after 21 days. a. Chest X-ray of the patients (only at the time of admission) b. Total and differential WBC count. c. Routine urine and stool. d. Routine Hb% e. Weight of the patients f. Clinical examination of the patients.
The patients were given Dekofcyn 2 tablets t.d.s. for one week at a time and they were assessed every week when they came to collect the tablets. The total duration of the treatment was for three weeks. The patients of the tubercular group were continued on anti-TB treatment which they were already receiving along with Dekofcyn. The non-tubercular group of patients were only on Dekofcyn tablets. The complete assessment. was made after three weeks of the treament.
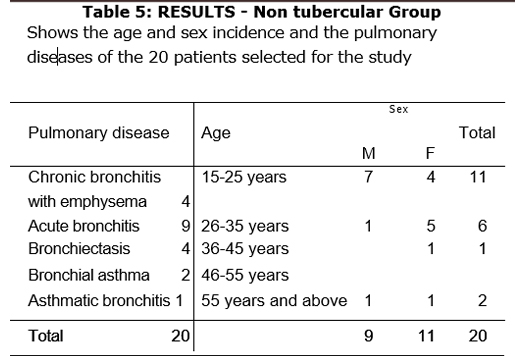
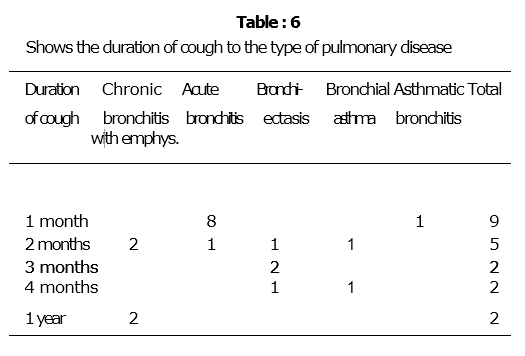
Out of 20 patients of non-tubercular group, there were 14 patients with expectoration and 6 with dry cough. Of the 14 patients with expectoration 7 patients showed complete absence of cough and 4 showed moderate improvement, while in 3 patients there was no improvement. Of the 6 patients with dry cough, 4 showed complete absence of cough and 1 showed moderate improvement, while in one patient there was no improvement.
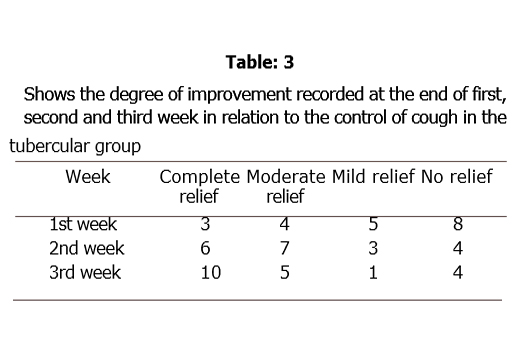
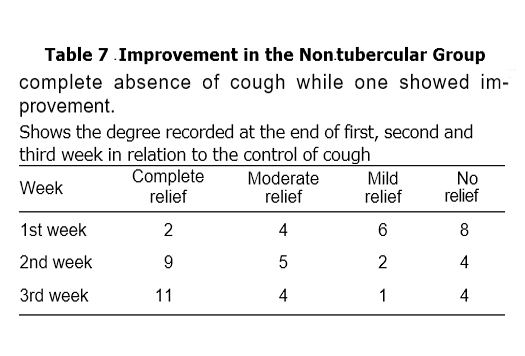
CHART I Showing relief in 1st, 2nd & 3rd weeks with DEKOFCYN treatment
1st week 2nd week 3rd week
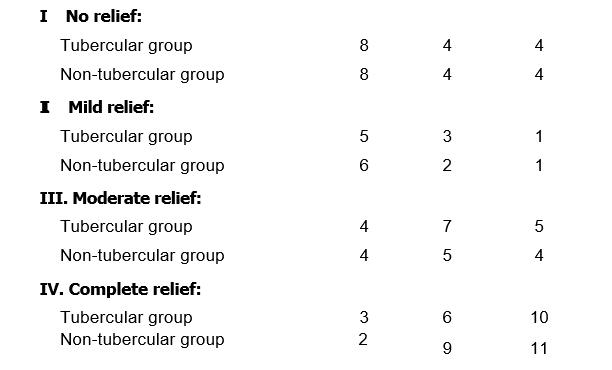
CONCLUSIONS:
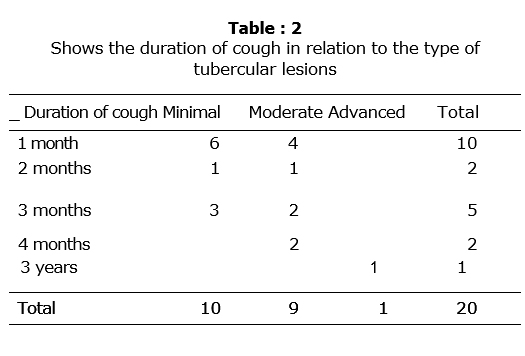
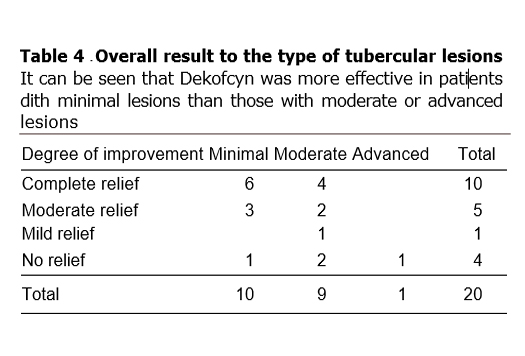
- 20 patients with pulmonary tuberculosis having cough for more than one month duration were given Dekofcyn for a period of three weeks, out of which 17 had expectoration and 3 had no expectoration. At the end of three weeks, it was found that 10 patients showed complete improvement, 5 showed moderate improvement and one showed mild improvement, along with decrease in expectoration. Patients also had a sense of well-being, 11 patients gained in weight of 1 kg. in three weeks. None of the patients showed any side effects to the drug.
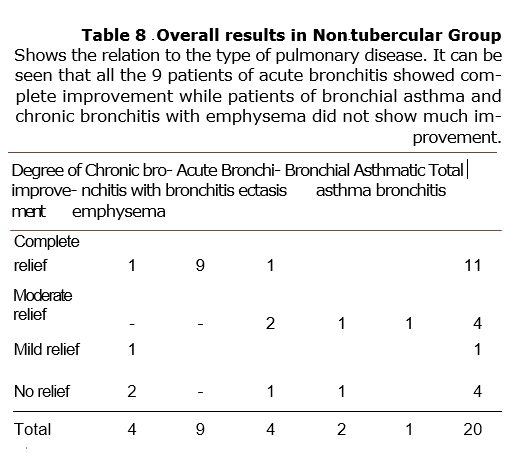
2. 20 patients with non-specific pulmonary diseases having cough for more than a month duration were treated with Dekofcyn for a period of three weeks, out of which 14 had expectoration and 6 had no expectora-tion. At the end of three weeks, it was found that 11 patients showed complete improvement, 4 showed moderate improvement and one showed mild improvement, along with decrease in expectoration. Of the 9 cases of acute bronchitis all showed complete improvement. Patients also had a sense of well-being, 8 patients had gain in weight of 1 kg in three weeks. None of the patients showed any side effects to the drug.
3. This study shows that Dekofcyn is very effective against chronic cough due to pulmonary tuberculosis and other non-specific conditions. It reduces frequency of cough and expectoration. This drug does not have any toxic effect and could be used safely.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: We thank the Dean, J. J. Group of Hospitals, Bombay, for allowing us to carry out the trial of this preparation. We thank the Messrs. Alarsin, Bombay, for assisting us in conducting the study.
REFERENCES:
- Chaudhari, S. N. Das: Current Med. Pract. 19:3, 119-123. March 1975.
- Gupta, J.P.: J. Chikitsak Parishad, 2:3:56-60, 1971.
- Mathur, J.B.L.: Ind. Prac., XX:6:409-410, 1967.
- Shah, B.N.: Paper at the 41st All India. Med. Conf. Baroda. Patna J. Med., 40:3:111, 1965.
- Sharma, D.D. Mah. Med., J. XXI, 11, 409-412, 1975
