Reprinted from The Bombay Hospital Journal, Vol. 22, No. 2, 1980 PP. 36-41
The usefulness of an Ayurvedic Drug containing Eupatorium Ayapana in 50 cases of Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding
J.KARUNA
Introduction
Dysfunctional Uterine bleeding is one of the commonest problems faced by Gynae colonists in India. The incidence is reported to vary from 12.6% to 23.1 %. Uterine bleeding occurring at unexpected times or in of normal menstrual flow in the absence of organic or systemic disease is defined as Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding.
Dysfunctional Uterine bleeding treated with haemostatics and hormones like oestrogen, progesterone, androgens, which on prolonged use, have a number of side effects. Here lies the usefuh1ess of an indigenous drug which is both safe and effective.
COMPOSITION OF EACH TABLET
| Ayapana (Eupatorium ayapana) | 60 mg |
| Asoka (Saraca indica) | 60 mg |
| Nagakesar (Mesua ferrea) | 30 mg |
| Godanti (Gypsum) | 30 mg |
| Kamboji (Breynia patens) | 90 mg |
| Jeevanti (Leptadenia reticulata) | 90 mg |
Ayapana herb contains an essential vo little oil and a neutral crystalline principle; its leaves contain an aromatic vola tile oil and the dried;l leaves yield not less than 0.05 % of the alkaloids, Ayapanin and Ayapin. Asoka bark contains a large amount of tannin and colouring matter haematoxylin catechol. Godanti, the hydrated calcium sulphate is having astrin gent and haemostatic properties. Nagakesar has antibiotic activity.
Material and Methods
The clinical trial was carried out in 50 patients aged 16 to 45 years, with an established history of dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Patients were selected from the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Government General Hospital, Guntur ( Andhra Pradesh) during the years 1972 and 1973.
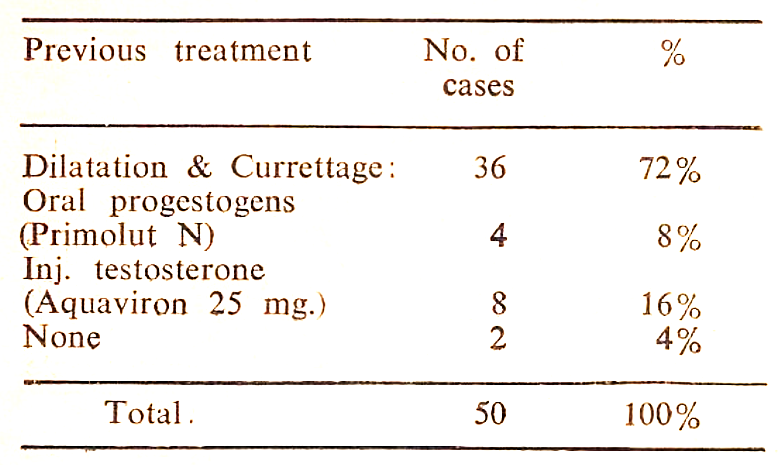
Before instituting the treatment, a thorough general and systemic examination and even dilatation and curettage were done to exclude any pathological condition of the uterus. Most of them had been previously treated on usual lines, i.e. Dilatation and curettage and hormones but with out benefit and the bleeding recurred. In each case, endometrial biopsy was taken to study the nature of the response of the endometrium at the end of the treatment. As a supportive treatment, haematinics and mulvitamins were given. Bed rest was advised during bleeding episodes.
DOSAGE
Those suffering from menorrhagia were given 2 tablets 3 times a day for 7 days, prior to the onset of menstruation; 11 cases of polymenorrhagia and 13 cases of metropathia were given one tablet 3 times a day for 30 days. In both the groups the treatment was given for 3 cycles. In 10 cases of continuous and irregular bleeding, they were given 2 tablets, three times a day, for 5 days. If necessary this was followed by the same dosage for another 5 days. The patients were asked to come to follow-up every month when a detailed history regarding the amount and duration of bleeding was noted. They were followed-up for a period of 6 months. If the pa tient did not respond to 3 months therapy, the treatment was continued for another three months. Patients who responded to treatment were observed for a further period of 6 months.
Results
The criteria for improvement were :
- Reduction in quantity of bleeding.
- reduction in duration of bleeding and
- change in irregularity of bleeding to wards normal.
Response
- Good : Complete relief of symptoms and reversal to regular periods. The bleed ing decreased within 3 days and subse quent menstrual rhythm was regularised from the next month. No irregularity was found within 6 months of observation.
- Fair : When bleeding decreased with in one week and ceased completely within 10 days and rhythm was regularised from third cycle onwards.
- Poor : When bleeding did not stop, in spite of 6 months course of therapy.
Obserfations and Analysis of Data
TABLE I
Histopatholo’gical findings of endometrium in 50 Patients. Most of the cases ((72%) showed proliferative phase.
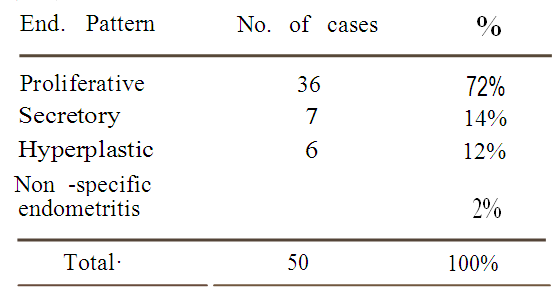
TABLE II
Menstrual History: Menorrhagia is the main pre senting symptom (32%).
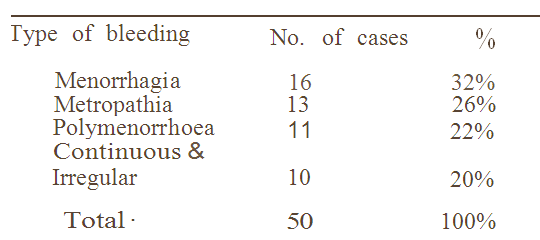
TABLE III
Duration of Bleeding
88% of Cases had the bleeding for more than 6 months.

TABLE IV
Parity Comparison With Other Authors
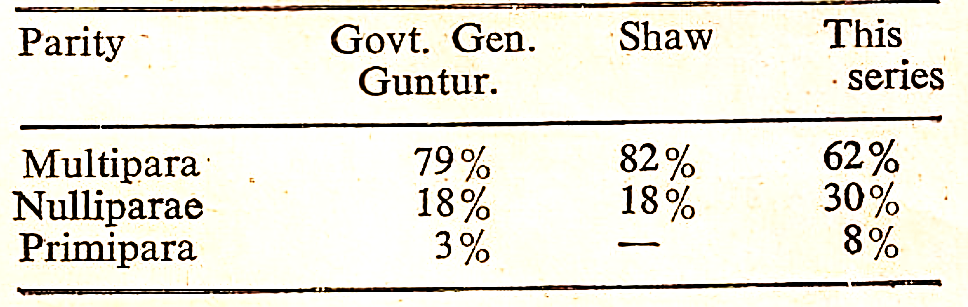
TABLE V
Distribution of Cases Among Different Reproductive Groups
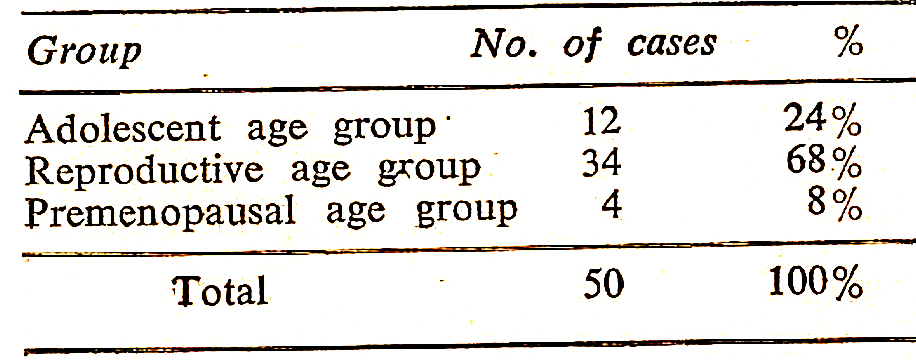
TABLE VI
Pelvic examination Findings

TABLE VII
Previous treatment
In 26 patients (52%) the response was good. All these patients responded after 3 months of therapy. 19 patients (38%) bad reduced bleeding after 4 months of therapy and got cured after 6 months therapy. Only 5 patients did not respond even to 6 months therapy. Out of these 5 patients, 3 were operated – 2 cases were of seed• ling fibroids and one case was of endomet rial polypoidosis. Out of the remaining 2 patients, one attained menopause and the other did not come af ter 6 months treat ment. On the whole, 45 patients (90%) responded favourably to treatment and had relief from their symptoms. (Table VIII).
TABLE VIII
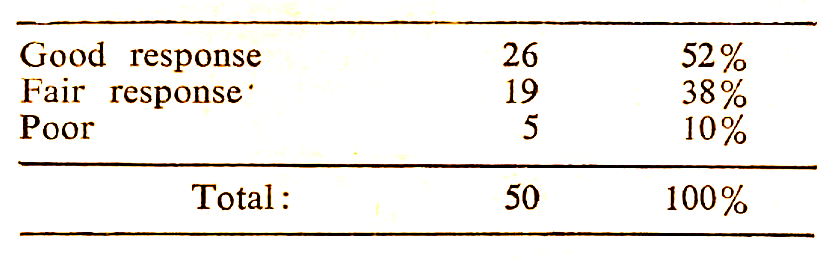
It was noticed that the patients who res ponded best were of those suffering from menorrhagia and metropathia. (Table IX).
TABLE IX

TABLE X

The endometrial biopsy was repeated after completion of therapy and it was found to be the same as before the treat ment and no change was observed in the endometrium.
Side Effects
Only one patient complained of exces sive nausea. No other side effect was no ticed.
Discussion
The multiplicity of methods of treatment employed for Dysfunctional Uterine Bleed ing evidence difficulties and disappoint ments. Styptics, various combinations of drugs and hormones including ovarian hormones, androgens, gionado1lrophins1, lacto gen, thyroid extract, pitressin, vitamins, antimenorrhagic factor of liver, raidiothe rapy and operations, have all been tried with varying claims of success by different workers.
In the absence of exact knowledge of the aetiology of dysfunctional uterine bleeding and also the unsatisfactory results of treatments, the value of this Ayurvedic preparation with its haemostatic properties, and with assimilable calcium causing coor dinated uterine contractions controlling excess of bleeding deserves attention. The present therapy showed encouraging re sults in 90 % of the patients in our series and proved helpful in some cases in avoid ing surgical and drastic drug treatment. Phadnis from Poona (1964), Mehta from Bombay (1964) and Javeri from Baroda (1965) and other authors have reported en couraging results with this therapy.
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
- The present study deals with the use of the combination containing E. Ayapana in the treatment of Dysfunctional Uterine Bleed ing of 50 cases.
- In all these cases, the endometrial pattern was studied by biopsy before and at the end of the course and no change was found in the endometrial
- Best results were obtained in cases of me
- There were no side effects with this drug except nausea in one
- The drug owes its effects to its haemostatic properties and uterine sedative action.
- The drug is non-hormonal, cheap, effective and
- The cure rate in the present series is 90% 45 patients out of 50 were cured within one to 6 months of therapy, (The treatment was given for 6 months only in 19 38%).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS :
My grateful acknowledgements to Dr. N. Subhdra Devi, M.D., FRCOG., Dr. A. V. Narayana Rao, M.D., Dr. A. Savitri, M.D.; Former Professors of Obstetrics & Gynaecology; Dr. C. Rani Hitavachani, M.D., Former Asst. Prof. of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, and Dr. Vani, M.D., student in Obstetrics and Gynaeco logy; Guntur Medical College and Gene.ral Hos pital, Guntur. I am thankful to Alarsm Phar-
maceuticals, Bombay, for the generous supply of the product containing Eupatorium Ayapana.
REFERENCES
- Bickers, Menorrhagia, Menstrual Dis tress, 1954.
- Bhattacharji, Saroj K; O. (Cal.), MRCOG, DGO. – “Dysfunctional Ute rine Haemorrhage – Correlation of En dometrial Pattern with Clinical Behaviour.”
- Journal of Obstotrics & Gynaecology of India, 14 of 1964, Page: 372-379.
- Browne J. and Browne J.C., Postgraduate Obstetrics & Gynaecology, 1973.
- Browne, Aleck, Wand Williams, Leslie
- Recent Advances in Obstetrics and
- Chakraborty, R.K., MD, DGO., and P. K. Devi, MS., FRCS., “Treatment of Puberty Menorrhagia with Hormones” – Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology of India, Vol. of 1970 Page 416-420.
- Charles Meleman – American Journal of Obst. & Gynec. Page 989-94: 1952.
- Chopra, R. – Indigenous Drugs of India, 2nd Ed. 1958.
- Claylee, Andrew and Browne : British
& Gynec.
9. Cope, E., MD, FRCOG : “PHYSIOLOGY OF ABNORMAL BLEEDING”, British Medical Journal, 5, June 1971 – P.573-575.
- Cope, Edward, MD., FRCOG : “Dysfunc- tional Bleeding” – British Medical Jour nal, 12, June 1971, P 631-632.
1 1. Cope, Edward, MD, FRCOG : “Manage- ment of Abnormal Bleeding” – British Me dical Journal – 19, June 1971; P:700-701.
- Darchman Isidore: American Jou rnal of & Gynec. 212-95 – 1966.
- Dass, Anasuya, MRCOG and S. Chugh, DGO.,: “Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding
- A clinico-pathological study” – Journal of & Gynec. of India : Vol. 14 No. of 1964 P: 348-354.
- Dass, Anasuya, and R. K. Popli, MBBS,: “Nor-Ethynod rel in Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding” (A Preliminary Report)
- Journal of & Gynec. of India, Vol. 14, of 1964, P: 431-439.
- Dawn, S., DGO., MO, D. Phil (Cal.) MRCOG (Lond) -“Environment and Dys· functional Uterine Haemorrhage”, Journal of Obst. & Gynec. Vol. 14 of 1964 P. 408· 412.
- Devi, K., MS, FRCS, and U.D. Sutaria MD, : “Functional Uterine Haemorrhage (A clinical and Histological study of 357 cases) – Journal of Obst. & Gynec of India, Vol. 14 of 1964 P: 355-359.
CLI NICAL TRIAL OF flFTY CASES OF DYSFUNCTIONAL UTERINE BLEEDING
- Dey, Bhaskar Lal, : “The study on the Hae mostatic Behaviour of Ayapana and a few notes on ” – Indian drugs, Sept. 1973 – P: 13-14.
- Fernandes, Winfred, MD, FCPS, and Kalyani Subrahmanyam, MD, DGO : “Gynaecological Problems in Teenagers”, Journal of Obst. & Gynec. of lndia, Vol. of 1971 P : 53-59.
- Fluhmann – The management of men strual
- Ghosh, K., MBBS, Dip. Borns., D. Phil Cal) and K.P. Sengupta , MBBS, D. P.1il (Cal.) – Journal of Obst. & Gynaec. of India, Vol. of 1968 P-310-316.
- Ghosh , R – Pha rmacology , Materia Me dica and Therapeutics 20th Edition,
- Hamblen- Endocrinology of womer>
- Jahagirdar, R., FRCS (Eng.), FRCS (Edin), “Place of indigenous d rug Ayapon in Dysfunctional uterine bleeding.” – Paper read at XVI Conference of Interna tional College of Surgeons, Hyderabad,
A.P. 2-4 Oct. 1970.
- Javeri (Sm ) Veenaben, MD, DGO, “Treat · ment of Functional uterine bleeding” A clinical study with Ayapon” – Indian Practitioner; Vol. 18, No. 1 1 1965 P: 783- 786.
- Jeffcoate TNA – Abnormal and Excessive Haemorrhage from the uterus and vagina in “Princi ples of Gynaecology” .
- Joshi, K ., MD. and D. H. Deshpande, MBBS. DB. (Born.) – “Clinico pathologica study in 274 cases of Dysfunctional Ut.::rine Haemorrhage” – Jou rnal of Obst. k Gynaec. of India, Vol. 14 of 1964 P : 360- 371.
- Kanakad urgamba MD, M RCOG and
- Srinivasarao, MD – “A clinical and histopathological review of Dysfunctiona l Uterine Bleeding (One h undred and fif ty cases) – Jou rnal of Obst. & Gynec. of India – Vol 1 4 of 1964 P380-386.
- Khan, , MD, MRCOG., “Dysfunction al uterine bleeding (Age group under 20 years”: Journal of Obst. & Gynec. of India, Vol. 14 of 1964 P393-396.
- Keller J. – Modem Trends in Gynae cology.
- Kodkany Kamal B., MD, FCPS, DGO. “Use of Ayapon in uterine bleeding after IUCD.” – The Ind ian Practitioner. Vol. 21 No. 12, Dec. 1968 P : 901 -903.
- Kupperma S – Diagnostic value cf Endometrium in Menstrual abnormalities. human endocrinology .
- Lewis, TLT: Progress in clinical Obstetrics &
- Mac Donald – Scientfiic basis of Obstet rics and
- Masani M. – Menorrhagia and D.U.B.
- Text Book of Gynaecology
- Mazer and Israel – Diagnosis and treat ment of Menstrual disorders and
- Mehra, , M.D.: P. K. Devi, MS, FRCS,
- N. Chakravarthi, MBBS, D. Phil and R. R. Chaudhury, MBBS, D. Phil; “Mast cells in the Endometrium in Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding and postabortal bleeding.”
- Journal of & Gynaec. of India, Vol. No. of 1970 P 792 to 794.
- Mehrotra, G. MD, Krishna Mukerjee MS; Manjula Pandey, MS and V. Samant, M D; “Functional U terine Bleeding – A review of 150 cases” – Journal of Obst.
& Gynaec. of India : Dec. 1972 Vol. 27 No. 6 P : 684-689.
- Meh taji Shirin : “Puberty Menorrhagia”
- Bom bay Hospital Journal, 12, No. 2, April 1970 P: 39-41.
- Meigs, Joe V and Sturgis, Somer H : Pro gress in Gynaecology, III.
- M. K. K rishna BA, MD, FRCOG : Ramani Sivaraman, MD, and K. Anasuya,
M BBS, DGO, “Carbohyd rate Metabolism i n Dysfunctional uterine bleeding.” – Jour
na l of Obst. & Gyn::iec. of lndia, Vol. 14 No. of 1964 P : 343-347.
- Misra, Ananta and Surya Narayan Misra : “Studies on the Haemostatic effect of f ‘UT indigenous d ” – Orissa Veteri n ary Journal , Vol . 3 No. I. 1965.
- Mitra, K.. MB. DGO. MO. (Cal.),
M RCOG. Pl”i D (Lond) – “A study of t he ovaries in Dysfunctional uterine haemorr hage”. – Journal of Obst. & Gynaec. of India, Vol. 14 No. of 1964, P.398-406.
- Mukherji, B – The Indian Pharmaceutic I
- Nad ka K M. – Indian Materia Med ica – 3rd Ed. 1954.
- Nanivadekar S., MD, M.Sc. “Ovral in menstrual disorders” current Medical Prac tice, Vol. l 7, No. 6, June 1974 P : 257-261 .
- Nayar, U and R . Bijlani, “Physiologkal basis of abnormal bleeding,”, Bomba ” Hos pital Journal, 14, No. I Jan. 1972 – P. 15-22.
- . Ed mund R and Jones G. 0. No vak ‘s Text Book of Gynaecology. 1,8. Novak, Emil – Novak’s Obstetrics & Gynaecological pathology.
Abstract of Part II of the thesis titled, “A Clinical & Histopathological study of Dysfunctional Ute rine Bleeding (J OO cases) and use of an Ayurvedic drug containing E. Ayapana in Dysfunctional Ute rine Bleeding (50 cases)” submitted for M.D. (Obst. & Gynec.) of the Andhra Un
